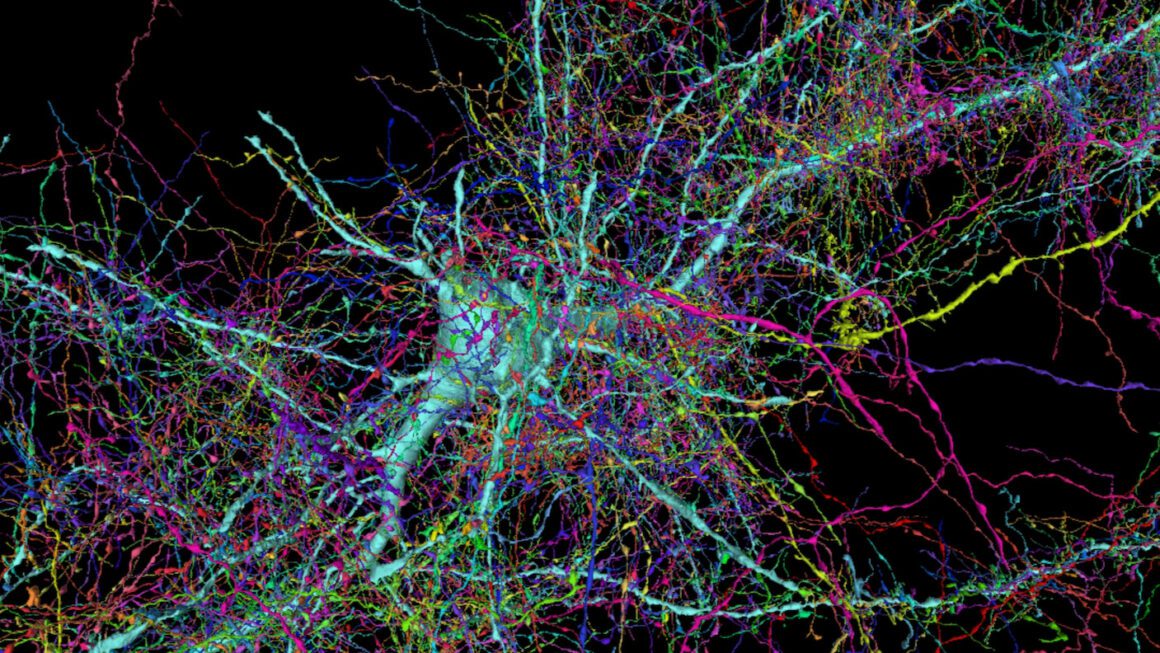
In an extraordinary leap for neuroscience, Harvard and Google researchers have unveiled the most comprehensive 3D reconstruction of human brain tissue ever created. This ambitious project, led by Harvard’s Jeff Lichtman and supported by Google’s AI capabilities, mapped a cubic millimeter of the brain’s temporal cortex in staggering detail, producing a dataset of 1,400 terabytes. This intricate map reveals 57,000 cells, 150 million synapses, and 230 millimeters of blood vessels, offering unprecedented insights into the brain’s architecture and function.
The Technological Marvel Behind the Map
The creation of this detailed brain map was no small feat. Using advanced electron microscopy, the team sliced the brain tissue into ultra-thin sections, each 30 nanometers thick. Google’s AI algorithms then stitched these sections together, producing a seamless 3D model. This combination of cutting-edge technology and meticulous scientific effort has resulted in a dataset that is both massive and incredibly detailed, allowing scientists to explore the brain’s inner workings as never before.
Implications for Neuroscience and Beyond
This groundbreaking work is poised to revolutionize our understanding of the brain. The map reveals rare structures, such as axons connecting via up to 50 synapses and unusual whorls, which could shed light on how the brain processes information. Furthermore, this detailed reconstruction has the potential to advance research into various neurological conditions, providing a new tool for scientists studying diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
Future Directions and Broader Goals
This project is part of the broader NIH BRAIN Initiative, which aims to map the entire mouse brain’s neural wiring, a project exponentially larger than the current human sample. Future efforts will focus on mapping the mouse hippocampal formation, crucial for understanding memory and learning. The publicly available dataset and analysis tools are expected to empower researchers worldwide, fostering collaboration and accelerating discoveries in brain science.
Expanding Perspectives from Additional Sources
- Nature Neuroscience: Highlights the implications of this dataset on understanding neurodegenerative diseases and neural plasticity. This detailed analysis emphasizes how this data can refine models of synaptic connectivity and neuronal behavior.
- National Institutes of Health (NIH): Discusses the broader goals of the BRAIN Initiative, aiming to map the entire mouse brain’s connectome. This source outlines future steps and potential breakthroughs in decoding complex neural circuits.
- Google AI Blog: Provides technical insights into the AI algorithms used to process and analyze the vast amounts of data, illustrating the cutting-edge technology behind the project.